Create Portfolio Maps
- Portfolio or value chain representations are a widely used instrument for presenting global interrelationships.
- This notation can be used to create a clear map of all management, core and support processes.
- Since the notation is not standardized, there is little need for training. It is also well suited for free modeling.
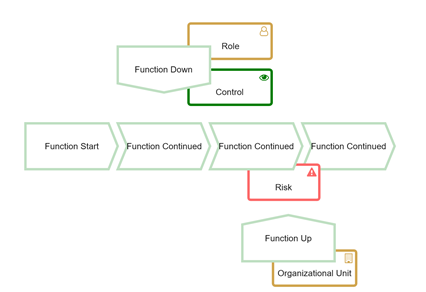
Symbol Overview
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
 | Management processes, that govern the operation of a system. Typical management processes include corporate governance and strategic management. |
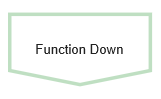
 | Operational processes, that constitute the core business and create the primary value stream. Typical operational processes are purchasing, manufacturing, marketing, and sales. |
 | Supporting processes, that support the core processes. Examples include accounting, recruitment, and technical support. |
 | Organization units determine which organization within the structure of an enterprise is responsible for a specific function. |
 | Organization unit assignments show the connection between an organization unit and the function it is responsible for. |
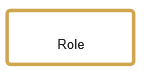 | The process owner is responsible for a function (i.e. a booking clerk is responsible for booking journeys). |
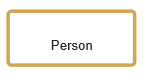 | The process owner is usually part of an organization unit (i.e. a booking clerk belongs to the booking department). |
 | The risk object is used to describe potential risks or dangerous situation. It is used to document any potential harms connected to a process step. |
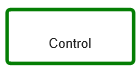 | Controls help to link checks and balances and ongoing monitoring tasks to the process. |